As we understand KAIZEN benefits, features, and principles in Previous blog http://KAIZEN Part-1in this blog we will discuss about Kaizen Process. KAIZEN process provides a disciplined and Analytical approach. Sometimes KAIZEN sounds like a problem-solving approach to solve the problem and improve the process. It consists of multiple steps or sequential steps that help to build a process to identify, analyse, and resolve the problem called PDCA ( Plan-Do-Act-Check).
7 Steps of the KAIZEN Process
- Defining the problem
- Assessment of the problem or current situation
- Finding the RC (Root Cause)
- Planning for Action
- Implement the Action
- Verify whether the problem is resolved or not
- Standardizing and Establishing process and control
Below the brief Flow chart on Problem detection Phase in KAIZEN Process
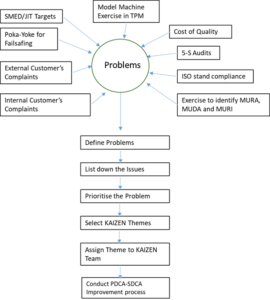
PDCA Activities
| # | Process Steps | Objective | Element of PDCA Cycle |
| 1 | Defining the Process | Identifying the problem based on criticality or Impact | The “PLAN” element |
| 2 | Assessment of the problem | Assess the issue and find the Gap for Improvement | -do- |
| 3 | Finding the RC (Root Cause) | Understand the Root cause of the problem | -do- |
| 4 | Planning for Action | Preparing Action Plan | -do- |
| 5 | Implement the Action | Implement the Action Plan | The “DO” element |
| 6 | Verify whether the problem is resolved or not | Confirm the result and Output | The “Check” element |
| 7 | Standardizing and Establishing process and control | Consolidating the change and make standard | The “ACT” + Standardize the SCDA |
PDCA in KAIZEN Process
Let’s understand the PDCA process in details:
-
Defining the Problem (Plan)
It can be included, but not limited to:
- GAP in performance
- Target issue
- Project running behind the Schedule,
- Deviation in Quality norm
- Increase defect rate
- Drop market share
- More customer complaints
- Unclear action plan to achieve target
-
Assessment of the problem (Plan)
It can be included, but not limited to:
- Connect with people, team, customer and observe the problem carefully.
- Initiate the necessary action plan based on critically and nature of the problem
- Perform Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
- Gathering of all related and supported data
-
Finding the RC (Root Cause) (Plan)
It can be included, but not limited to:
- RCA is a central tenet of KAIZEN.
- Intend to ensure that we are working on right cause or problem statement
- Why-Why Analysis
-
Planning for Action (Plan)
It can be included, but not limited to:
- Involved required team members to plan to mitigate the problem
- Need to use tool like Fishbone analysis
- Brainstorming
-
Implemented the Action (DO)
It can be included, but not limited to:
- Take logical step to implement to action planned
- Time line to implement the solution
-
Verify whether the problem is resolved or not (Check)
It can be included, but not limited to:
- Check & verify if the action plan works
- Check & verify if the problem resolved
- Check & verify if there are positive response from customer
-
Standardizing and Establishing process and control (Act)
It can be included, but not limited to:
- If problem is resolved and working then next step to make a standard
- Once problem resolved then Moved from PDCA to SDCA
- SDCA to make ensure that standards process should continue deliver.
SDCA- Standardize-Do-Check-Act
S of SDCA is refer as Standardize, monitoring, supervision and operation to maintain standard process
D of SDCA is refer as DO- people assure that they adhering the standard method.
C of SDCA is refer as Check- to assure that by continuing to adhering or following the standard do we delivering the Output as specified.
A of SDCA is Act – to assure to take appropriate action if desire results are not achieved.
Conclusion
In KAIZEN PDCA is nothing but Plan-DO-Check-Act to identify the problem and work on root cause of the problem to resolve it.
SDCA is particularly useful when problem is resolved than it require to make standard process to follow to avoid the repletion of such problem. Standards stands for “Right Way of doing a task”.
Both PDCA and SDCA are iterative, and the idea is to continually cycle through them to drive ongoing improvements in an organization or system. These methodologies are key components of the Kaizen philosophy and are widely used in Lean manufacturing and other quality improvement approaches.
(Source: SCDL, Techniques for Operation Efficiency)
Visit to our site : https://www.kbrosistechnologies.com/
Watch more Video https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCpcd6IshE1caAbf9EdJd3gw



