ITIL-Information Technology Infrastructure Library, is a broadly known for ITSM framework that provides best practices for IT service management. It defines a set of practices, Guidelines and processes to help organizations align their IT services with their business needs. ITIL v4 is the latest version of the ITIL framework, released in 2019.
Introduction
As we all know, how fast technology is growing, it will be not wrong to say that, almost every day we introduced with new technology, like Cloud, AI, Robotics, ML, Blockchain etc. some of technology we adopt some of not, but it’s a fact that world is changing with technology. But along with technology growth its requires more process and practices to manage to ensure that they remain relevant and successful and it, the most widely adopted guidance on IT service management (ITSM) in the world. ITIL 4, which was introduced in 2019, represents a significant evolution of the framework compared to its predecessor, ITIL v3.
It’s leading ITSM industry with guidance, training, and certification programmes from last 3 decades. It brings ITIL up to date by re-shaping much of the established ITSM practices in the wider context of customer experience, value streams, and digital transformation, as well as embracing new ways of working, such as Lean, Agile, and DevOps.
Why ITIL required
Information Technology Infrastructure Library is a widely adopted framework for IT service management. Mainly it required for:
Improved Service Delivery
It offers a organized method to managing IT services, ensuring that they are aligned with business goals and customer needs. By applying this practices, organizations can improve:
- Service delivery,
- Improve service quality,
- Increase customer satisfaction.
Efficient Incident and Problem Resolution
It offers procedures and practices for incident management and problem management, enabling organizations to handle and resolve issues effectively & efficiently. This reduces the impact of incidents on business operations and helps identify the issue proactively and address the root causes of problems
Effective Change Management
It provides rules for change management, which helps organizations plan, assess, and implement changes in a controlled and organised manner. This reduces the risk of service disruptions and ensures that changes are aligned with business requirements in term of Normal, standard, Major, Critical and Emergency changes.
Enhanced Service Level Management
It accentuates the importance of service level management-SLA, enabling organizations to define, negotiate, and monitor service level agreements (SLAs) with customers. This ensures that services are delivered according to agreed-upon standards, leading to improved service performance and customer satisfaction.
Optimal Resource Utilization
It helps organizations improve resource allocation and utilization as well by capacity management, it help us aligned resources with business needs, leading to cost savings and improved efficiency for better resource utilizations.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is very essential part of any organisation. To business suitability business improvement is required. It promotes a values of continual service enhancement. By implementing the continual improvement model and adopting practices such as monitoring, measuring, and analysing service performance, organizations can identify areas for enhancement and drive ongoing improvement in service delivery and processes.
Professional Development
ITIL certifications provide individuals with a globally recognized qualification in IT service management. By acquiring ITIL certifications, professionals can enhance their knowledge and skills, making them more valuable to employers and opening up career opportunities.
ITIL-V3 Service Lifecycle vs ITIL-V4 Service Value System (SVS)
In ITIL-V3, Service Lifecycle is a key concept in ITIL and it representing the stages through which a service progresses from start to end. The ITIL v3 framework presented the thought of the Service Lifecycle, which has been further distinguished and reformed in ITIL 4. The ITIL Service Lifecycle consists of five core stages:
- Service Strategy
- Service Design
- Service Transition
- Service Operation
- Continual Service Improvement
It is an iterative and continuous process. Each stage contributes to the overall management and improvement of IT services. The lifecycle approach ensures that services are tactically planned, well-designed, effectively transitioned, and continually improved throughout their lifespan.
In ITIL 4, the concept of the Service Lifecycle has been prolonged and integrated into the wider concept of the Service Value System (SVS), which incorporates additional essentials such as governance, practices, and the four dimensions of service management. The SVS provides a holistic view of service management in the context of value creation and co-creation with customers.
ITIL v4 service value system (SVS)
The key components of the ITIL 4 framework are the service value system (SVS) and its four dimensions model, which we discuss in this blog.
SVS (Service Value system) represents the various components and activities/system of the organization work together to facilitate value creation through IT-enabled services. It introduces a holistic approach that emphasizes delivering value to customers through IT services.
The SVS encompasses various components, including the
- Service Value Chain,
- Practices
- Guiding principles,
- Governance
- Continual improvement.
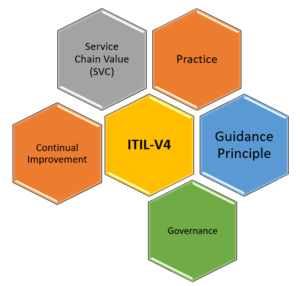
Service Value Chain (SVC):
The Service Value Chain is a core component of the SVS, consisting of interconnected activities that create value for customers. The six activities in the SVC are Plan, Improve, Engage, Design & Transition, Obtain/Build, and Deliver & Support. Each activity represents a set of practices and processes that contribute to the creation and delivery of IT services.
Practices:
It introduces a flexible and modular approach to practices. It offers 34 management practices categorized into three types: general management practices, service management practices, and technical management practices. These practices provide organizations with a toolkit to manage various aspects of IT service delivery, such as incident management, problem management, change control, and service level management.
Guiding Principles:
The SVS is guided by a set of seven principles that serve as the foundation for decision-making and actions. These principles include focusing on value, starting where you are, progressing iteratively with feedback, collaborating and promoting visibility, thinking and working holistically, keeping things simple and practical, and optimizing and automating.
Governance:
Governance ensures that the IT service provider operates in a controlled and compliant manner while delivering value to stakeholders. It defines the policies, rules, and decision-making processes to use best of IT Business.
Continual Improvement:
Continual improvement is a fundamental aspect of the SVS. It emphasizes the need for organizations to evaluate their services, processes, and practices regularly or a Span of time and seek opportunities for enhancement. Continual improvement activities, guided by feedback and insights, help organizations optimize their service management capabilities and deliver increasing value to customers.
FAQ
Q1: What is the main difference between ITILv3 & ITILv4?
A: The main difference is structure and approach. ITIL v3 follows a 5-stage Service Lifecycle, while ITIL v4 introduces the Service Value System (SVS), which is a more holistic and flexible framework. ITIL v4 also emphasizes a value-oriented approach, integrating guiding principles, practices, and the four dimensions of service management.
Q2: Are the ITIL v3 processes still relevant in ITIL v4?
A: ITIL v4 announces a flexible approach to practices, allowing organizations to adapt their selection and adoption. While the specific processes in ITIL v3 are not clearly defined in ITIL v4, many of the concepts and principles remain relevant. Organizations can influence their existing ITIL v3 processes and adapt them to fit the updated ITIL v4 framework.
Q3: What is ITILv4?
A: ITILv4 is the latest version of the ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) framework released in 2019 It is a broadly accepted a set of best practices for IT service management.
Q: What is the Service Value Chain?
A: The Service Value Chain is a set of inter-connected activities that organizations can use to create value. It consists of six activities: Plan, Improve, Engage, Design and Transition, Obtain/Build, and Deliver and Support.
Q: What is the Service Value System (SVS)in V4?
A: The Service Value System (SVS) is the essential component of ITIL v4. It provides a flexible operating model for the creation, delivery, and continual improvement of services. The SVS includes inputs, outputs, activities, and components that work together to enable value creation.
Read More : https://techblog.kbrosistechnologies.com/
Visit to our site : https://www.kbrosistechnologies.com/
Watch more Video https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCpcd6IshE1caAbf9EdJd3gw

